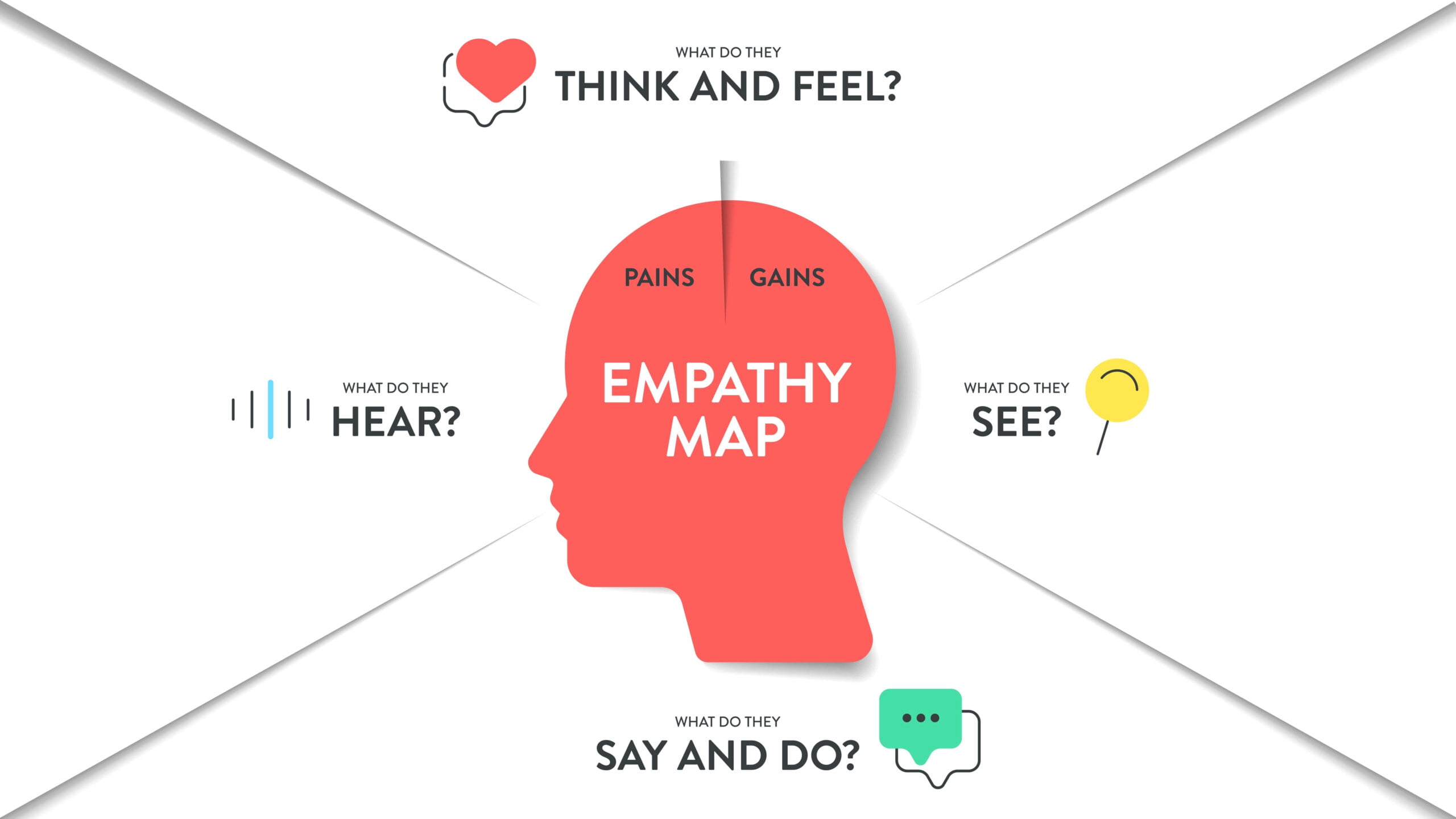
VR Empathy: Embracing Others’ Perspectives Through VR
Table of Contents:
Despite being relatively new, virtual reality has quickly proven to be a powerful educational tool. VR training is already widely used. Training in empathy and understanding other people’s perspectives is one area where VR can bring great success. Let’s follow the scientific research on this topic to better understand the benefits and effects of such training.
Can a Person Learn Empathy by Using Virtual Reality?
How can VR training help develop empathy and perspective-taking skills? To build positive interpersonal bonds, empathy is inextricably linked to prosocial behavior. Society and individuals function harmoniously when these bonds are present.
Researchers and training participants agree that VR environments are ideal for practicing empathy and taking the perspective of others. “Building long-term empathy: A large-scale comparison of traditional and virtual reality perspective-taking” conducted by scientists at Stanford University in 2018, is an example of documented research on this subject.
Empathy is a complex psychological trait that requires individuals to engage with and understand the emotional states of others. Studies have shown that cognitive empathy (the ability to understand someone else’s perspective) and affective empathy (the ability to share the emotions of others) are both enhanced through VR experiences. The immersive nature of VR allows users to “step into someone else’s shoes,” enabling them to feel and experience situations as if they were the other person. According to scientific research, this type of experience is much more powerful than traditional empathy exercises because it taps into both the cognitive and emotional centers of the brain simultaneously, enhancing the learning process. The intense emotional engagement provided by VR accelerates the development of these empathy skills, making the training far more effective than theoretical learning or simple role-playing.
Empathy, Perspective-taking, and VR Training
A study describing the results was published in the scientific journal Plos One. It was assumed that empathy and perspective-taking are two key aspects of building understanding and bonds between people that can be strengthened by VR training. Scientists defined empathy as understanding and sharing another’s feelings, while perspective-taking as an ability to see the world from one’s perspective. Based on their prejudices toward homeless people and people of different ethnicities, participants were evaluated on both values.
VR training enhanced participants’ empathy and perspective-taking skills in several ways, according to the study. Those who completed eight weeks of perspective tasks showed more positive attitudes and signed more petitions supporting homeless initiatives than those who only imagined being homeless or completed less involved perspective tasks.
The Perspective of Others in VR Simulations
An additional study, also conducted by Stanford University, shows that virtual reality increases cognitive empathy for others. Based on the research mentioned above, this study concluded that virtual reality experiences can increase prosocial behavior. In a series of games, partners were tested on their ability to adopt the perspective of their partner when faced with normal life situations, such as helping someone with communication issues who has difficulties reading or using a wheelchair. Participants interacted with a partner – a student from the same university – in a registered laboratory experiment.
Experimental results confirmed that VR training increased participants’ subsequent tendency to adopt their partner’s perspective (an aspect of empathy). However, this happened when the partner was the same person whose perspective the participants took in the virtual reality simulation. This confirms the theory that VR can enhance the ability to take a goal-specific perspective.
Real-World Applications of VR Empathy Training
The potential applications of VR empathy training extend beyond research settings and have already been implemented in various industries. For example, healthcare professionals use VR simulations to better understand the experiences of their patients. This can help nurses, doctors, and caregivers develop a deeper empathy for patients who are in pain, have limited mobility, or face mental health challenges. Similarly, in law enforcement, VR training programs have been used to help officers develop empathy toward individuals from diverse socio-economic backgrounds, improving their approach to conflict resolution and community engagement. These real-world implementations show how VR can play a significant role in creating more empathetic, socially responsible professionals who are better equipped to handle diverse and challenging situations.
VR and Everyday Challenges: Benefits
Studies on the development of empathy skills and taking the perspective of others using VR strongly confirm the benefits of VR. According to researchers, VR training offers participants the following benefits:
- Increasing empathy and perspective-taking skills;
- Improving communication and cooperation;
- Developing new strategies for resolving conflict.
VR can also be used in training aimed at developing empathy in an extremely wide variety of ways. Among them are:
- Simulations: Users can experience different situations from the perspective of different people, e.g. a homeless person, a refugee or a disabled person.
- Interactive games: VR games can teach cooperation and bonding between people from different backgrounds.
- Stories: VR can be used to tell stories from different perspectives, which can help users develop empathy for different social groups.
VR offers enormous possibilities for increasing empathy and learning to take a different perspective. As a society, we can be optimistic about reducing prejudice and promoting appropriate social attitudes as technology advances.
Measuring the Effectiveness of VR Empathy Training
To truly assess the impact of VR empathy training, it is crucial to measure its effectiveness over time. Traditional training methods often rely on surveys and self-reports to gauge improvement, but VR training offers the unique advantage of providing quantifiable data on participants’ emotional and behavioral responses. By using biometric sensors such as heart rate monitors and facial recognition software, trainers can track participants’ physiological reactions during the simulations, providing real-time insights into their emotional engagement. Furthermore, follow-up surveys and interviews can be conducted to assess how well these newly acquired empathy skills are transferred to real-world situations. Combining these objective data points with subjective feedback ensures a comprehensive understanding of the training’s effectiveness and its long-term impact on behavior.
Key Takeaways
VR training significantly enhances empathy and perspective-taking skills by immersing participants in realistic scenarios that engage both emotional and cognitive aspects of learning. Studies, such as those conducted by Stanford University, show that VR is more effective than traditional methods, improving empathy and prosocial behavior. VR is already used in industries like healthcare and law enforcement to help professionals better understand and engage with people from diverse backgrounds. VR training is versatile, simulating real-world situations that allow users to step into someone else’s shoes, fostering understanding and reducing prejudice. The use of biometric sensors and AI in VR training allows for measurable improvements and personalized feedback, ensuring effective skill development. Additionally, VR is more cost-effective and time-efficient than traditional training methods, providing a scalable solution for organizations to develop critical soft skills. As technology evolves, the potential for VR in empathy training continues to grow, offering even more personalized and impactful learning experiences.
Can a person learn empathy by using virtual reality (VR)?
Yes, VR is a highly effective tool for learning empathy. By immersing users in realistic scenarios where they can experience situations from another person’s perspective, VR helps them develop a deeper emotional connection and understanding of others’ feelings and circumstances.
What are the benefits of VR for developing empathy and perspective-taking skills?
VR allows participants to fully immerse themselves in another person’s perspective, fostering a deeper understanding of their feelings and emotions. This helps improve both **cognitive empathy** (understanding someone else’s point of view) and **affective empathy** (sharing their emotions), enhancing prosocial behavior in real-world situations.
How effective is VR empathy training compared to traditional methods?
VR empathy training has been shown to be significantly more effective than traditional methods like role-playing or theoretical exercises. The immersive nature of VR provides real-time emotional engagement, which accelerates the development of empathy and perspective-taking skills, making the training more impactful and memorable.
What industries are using VR for empathy training?
VR empathy training is used in various industries, including **healthcare**, **law enforcement**, and **customer service**. In healthcare, it helps professionals develop empathy for patients with diverse needs. In law enforcement, it aids in improving interactions with individuals from various socio-economic backgrounds, fostering better conflict resolution and communication skills.
How does VR training improve empathy and communication?
VR training improves empathy by allowing participants to experience scenarios from another person’s point of view, such as being homeless, disabled, or from a different cultural background. This immersive experience encourages deeper emotional responses, improving **communication** and **cooperation** as individuals learn to engage with others more thoughtfully and empathetically.
How is the effectiveness of VR empathy training measured?
The effectiveness of VR empathy training can be measured using **biometric sensors**, such as heart rate monitors and facial recognition software, which track emotional responses during training. Additionally, follow-up surveys and real-world behavior assessments are conducted to determine how well the acquired empathy skills transfer to everyday situations and workplace interactions.

Author: Rafał Siejca
Rafal has over twenty years of corporate experience, including roles at Millennium Bank, Comarch, and leading software teams at PZU, one of Europe’s largest insurance companies. As one of Poland’s few true VR experts with a decade of experience, he ensures timely, high-quality project delivery as CEO and CTO.